Transparent Encryption for Kubernetes
To get started with running CipherTrust's Transparent Encryption connector with Kubernetes, you would need to first have a deployed CipherTrust Manager instance. To learn about how to deploy CipherTrust Manager, check out our guides.
Kuberenetes Setup
There are some pre-requisites we need to check. Our VM must have installed versions of:
- KVM
- Docker
- Kubernetes
- helm
- Minikube
- Git
- A Kubernetes cluster health monitoring tool
Note: If you prefer, you could also perform this deployment with microK8s. This would remove the need to install services like MiniKube, KVM, Kubernetes, etc
Deploy CTE for Kubernetes
Once you have confirmed you have the pre-requisites to deploy CTE for K8s. You can run a test setup with an open-source demo by Thales. Run,
git clone https://github.com/thalescpl-io/ciphertrust-transparent-encryption-kubernetes.git
cd ciphertrust-transparent-encryption-kubernetes/
./deploy.sh
Configuring CipherTrust to talk to the Kubernetes Cluster
First, we need to generate a new registration token on the CipherTrust platform. We can do this by going to Access Management -> Registration Token -> "Add Registration Token"
We also need to enable the CipherTrust trial license, we can do this by going to Licensing -> "Add CipherTrust Platform Evaluation" to enable the evaluation license.
Setup the K8s Client
Go to
Clients -> K8s Storage Group. Create a new K8s storage group.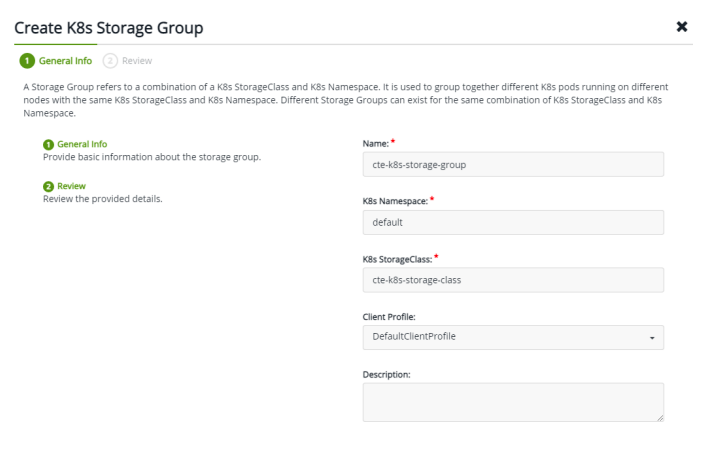
Go to
Policies -> Create Policynamedpolicy1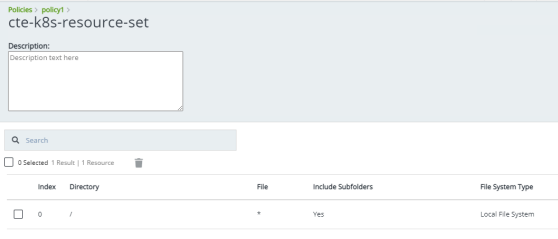
Permissions to set
- Action:
all_ops - Effect:
permit, audit, applykey
- Action:
Create a new
CBC-CS1key, and bind it to the resource setcte-k8s-resource-set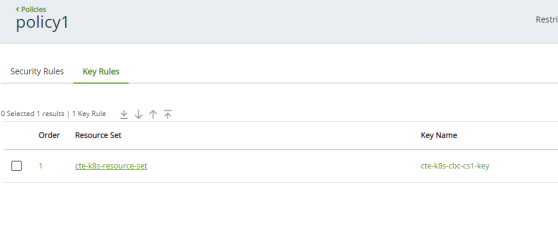
Finally, click on Create Policy!
Configure an NFS volume to protect your file system
- Create a shared folder for the NFS
sudo mkdir –p /usr/nfs/cte-k8s
- Specify the share location to export
sudo vim /etc/exports
## Add the following line to the file
/usr/nfs/cte-k8s *(rw,sync,no_root_squash)
Save the file and run
sudo exportfs –a
Start the NFS service
sudo systemctl enable nfs && \
sudo systemctl start nfs && \
sudo systemctl enable rpcbind && \
sudo systemctl start rpcbind
Configure the NFS volume in the Kubernetes cluster
Create the following files
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: nfs-test-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: nfs
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
mountOptions:
- hard
- nfsvers=4.0
nfs:
path: /usr/nfs/cte-k8s/
server: 10.10.10.7
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: nfs-test-claim
spec:
storageClassName: nfs
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
Update the following files accordingly
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: cte-k8s-storage-class
provisioner: csi.cte.cpl.thalesgroup.com
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
allowVolumeExpansion: true
parameters:
# Domain name or IP address of the CiperTrust Manager (Required)
key_manager_addr: <CM_INSTANCE_IP> #This IP address is the CM internal IP address
# Name of the CipherTrust Manager K8s Storage Group. (Required)
k8_storage_group: cte-k8s-storage-group
# Kubernetes Secret with CM registration token (Required)
registration_token_secret: demo #This name needs to be the same name of the registration token in CM
client_description: "Azure CTE k8s client"
# Time in minutes to wait before unregistering from the CiperTrust Manager
# once all volumes have been unguarded. Parameter must be added as a string
# integer value. Default "10" minute. (Optional)
registration_period: "10"
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: demo #This is the name of the registration tokens from CM dashboard for CTE k8s
type: Opaque
data:
# This is a base64 encoded registration token. To generate:
# echo <CM REGISTRATION TOKEN STRING> | base64 -w 0
registration_token: <YOUR_REG_TOKEN>
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: cte-claim
annotations:
# CTE for Kubernetes GuardPolicy name. This GuardPolicy is located on the
# CipherTrust Manager and should match a policy name available on the
# storage class for this PVC. (Required)
csi.cte.cpl.thalesgroup.com/policy: policy1
# Name of the unprotected source PVC that will be protected by this CTE-PVC.
# (Required)
csi.cte.cpl.thalesgroup.com/source_pvc: nfs-test-claim
spec:
storageClassName: cte-k8s-storage-class
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
# This parameter is required by Kubernetes but ignored by CTE-CSI.
storage: 1Gi
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: cte-csi-demo
spec:
volumes:
- name: test-vol
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: cte-claim
containers:
- name: ubuntu
image: ubuntu
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/data"
name: test-vol
command:
- "sleep"
- "604800"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always
Deploy all YAML files
kubectl apply -f nfs-pv.yaml
kubectl apply -f nfs-claim.yaml
kubectl apply -f cte-csi-regtoken.yaml
kubectl apply -f cte-csi-storageclass.yaml
kubectl apply -f cte-csi-claim.yaml
kubectl apply -f cte-csi-demo-pod.yaml
Verify deployment status
kubectl get all
kubectl get pod, pv, pvc
kubectl get pod –namespace=kube-system
Get Pod, PV, and PVC details
kubectl describe pod <pod name>
kubectl describe pv <pv name>
kubectl describe pvc <pvc name>
Now your data should be secured by CTE for K8s connector. You can verify this by going into the pod and creating a new file in the /data folder and verify that it is encrypted on the NFS from your local system.